Bootstrap Layout Responsive
Overview
In the last several years the mobile gadgets turned into such considerable element of our lives that almost all of us simply cannot certainly visualize just how we had the ability to get around without having them and this is definitely being said not simply just for getting in touch with some people by communicating just as if you remember was certainly the primary role of the mobile phone but in fact getting in touch with the entire world by having it straight in your arms. That's why it likewise came to be extremely important for the most common habitants of the Online world-- the website page have to showcase just as excellent on the small mobile displays as on the ordinary desktops that on the other hand got even bigger helping make the size difference also larger. It is supposed someplace at the beginning of all this the responsive systems come to appear supplying a handy approach and a variety of clever tools for having webpages behave regardless of the gadget viewing them.
But what's quite possibly vital and lays in the foundations of so called responsive website design is the strategy itself-- it is really entirely various from the one we used to have certainly for the corrected width pages from the very last several years which in turn is very much similar to the one in the world of print. In print we do have a canvas-- we set it up once in the start of the project to improve it up probably a several times as the work goes on but near the bottom line we finish up with a media of size A and artwork with size B placed on it at the defined X, Y coordinates and that is really it-- right after the project is completed and the sizes have been aligned it all ends.
In responsive website design but there is no such thing as canvas size-- the possible viewport dimensions are as pretty much unlimited so establishing a fixed value for an offset or a dimension can possibly be great on one display however quite annoying on another-- at the other and of the specter. What the responsive frameworks and especially one of the most popular of them-- Bootstrap in its own most recent fourth version present is certain smart ways the web pages are being created so they systematically resize and also reorder their particular components adjusting to the space the viewing screen provides and not flowing far away from its own width-- in this manner the site visitor reaches scroll only up/down and gets the web content in a convenient dimension for reading without having to pinch focus in or out to see this component or another. Let us see ways in which this generally works out.
Tips on how to use the Bootstrap Layout Template:
Bootstrap includes a number of components and alternatives for laying out your project, incorporating wrapping containers, a strong flexbox grid system, a versatile media object, and also responsive utility classes.
Bootstrap 4 framework employs the CRc system to handle the web page's content. Supposing that you are definitely simply starting this the abbreviation keeps it much simpler to remember considering that you will probably in certain cases wonder at first which element contains what. This come for Container-- Row-- Columns that is the structure Bootstrap framework employs intended for making the web pages responsive. Each responsive website page includes containers holding usually a single row along with the required number of columns within it-- all of them together forming a special web content block on webpage-- like an article's heading or body , list of material's functions and so forth.
Let us have a look at a single content block-- like some elements of whatever being actually listed out on a web page. First we really need covering the entire item in to a .container it is actually form of the small canvas we'll place our web content within. What the container performs is limiting the width of the area we have available for placing our web content. Containers are set to extend up to a particular width according to the one of the viewport-- regularly remaining a little bit smaller keeping a bit of free space aside. With the alteration of the viewport size and feasible maximum size of the container element dynamically transforms as well. There is one more type of container - .container-fluid it always expands the entire width of the presented viewport-- it's applied for producing the so called full-width page Bootstrap Layout Header.
Next inside of our .container we need to apply a .row element.
These are utilized for handling the positioning of the material features we set in. Since newest alpha 6 version of the Bootstrap 4 system applies a styling method called flexbox with the row element now all sort of positionings setup, grouping and sizing of the web content may possibly be attained with just providing a basic class but this is a whole new story-- for now do know this is the component it's performed with.
Lastly-- into the row we must place some .col- components that are the real columns holding our valuable web content. In the example of the elements list-- each attribute gets set inside of its personal column. Columns are the ones that operating with the Row and the Container elements generate the responsive activity of the web page. Things that columns ordinarily do is showcase inline to a certain viewport width getting the defined section of it and stacking over each other whenever the viewport obtains smaller sized filling the whole width readily available . So supposing that the display screen is bigger you have the ability to view a handful of columns each time but if it gets way too small-sized you'll see them one by one so you don't need to stare reviewing the material.
Simple formats
Containers are one of the most essential design component in Bootstrap and are called for whenever utilizing default grid system. Select from a responsive, fixed-width container ( indicating its max-width changes with each and every breakpoint) or fluid-width ( suggesting it is actually 100% large constantly).
Even though containers can possibly be embedded, many Bootstrap Layouts formats do not demand a nested container.

<div class="container">
<!-- Content here -->
</div>Operate .container-fluid for a total width container, spanning the whole size of the viewport.

<div class="container-fluid">
...
</div>Have a look at certain responsive breakpoints
Due to the fact that Bootstrap is created to be definitely mobile first, we use a fistful of media queries to make sensible breakpoints for layouts and interfaces . These kinds of breakpoints are typically based upon minimum viewport sizes and make it possible for us to size up components just as the viewport modifications .
Bootstrap mostly employs the following media query ranges-- or else breakpoints-- in Sass files for layout, grid system, and elements .
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Considering that we write source CSS in Sass, all Bootstrap media queries are available by means of Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We once in a while employ media queries which proceed in the additional course (the provided screen size or smaller):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthAgain, these particular media queries are additionally readily available via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are likewise media queries and mixins for targeting a specific sector of display sizes using the minimum required and maximum breakpoint widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...These types of media queries are additionally offered via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...In the same way, media queries may extend numerous breakpoint widths:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...The Sass mixin for targeting the similar display screen size range would certainly be:
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Z-index
A couple of Bootstrap elements implement z-index, the CSS property which supports command format by supplying a 3rd axis to set up web content. We incorporate a default z-index scale inside Bootstrap that is simply been created to appropriately level navigation, popovers and tooltips , modals, and much more.
We do not motivate customization of such values; you change one, you likely need to transform them all.
$zindex-dropdown-backdrop: 990 !default;
$zindex-navbar: 1000 !default;
$zindex-dropdown: 1000 !default;
$zindex-fixed: 1030 !default;
$zindex-sticky: 1030 !default;
$zindex-modal-backdrop: 1040 !default;
$zindex-modal: 1050 !default;
$zindex-popover: 1060 !default;
$zindex-tooltip: 1070 !default;Background components-- just like the backdrops which allow click-dismissing-- often tend to reside on a low z-index-s, whilst navigation and popovers incorporate higher z-index-s to assure they overlay surrounding web content.
Another advice
Utilizing the Bootstrap 4 framework you have the ability to set up to 5 various column appearances baseding on the predefined in the framework breakpoints yet ordinarily a couple of are quite sufficient for attaining best visual aspect on all displays.
Final thoughts
So currently hopefully you do have a general concept what responsive website design and frameworks are and just how the most famous of them the Bootstrap 4 framework manages the webpage material in order to make it display best in any screen-- that is actually just a short glimpse yet It's believed the knowledge just how the things work is the best basis one should get on right before searching in to the details.
Examine a number of video clip training regarding Bootstrap layout:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap layout authoritative documentation

A strategy within Bootstrap 4 to specify a intended layout
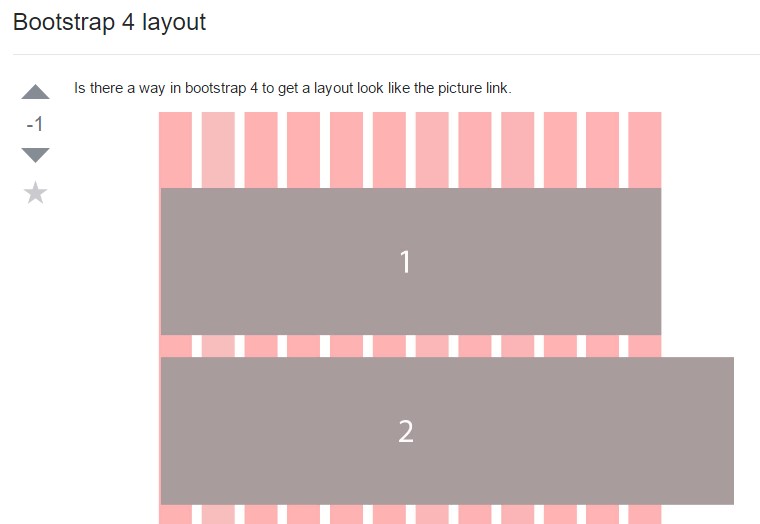
Style illustrations in Bootstrap 4